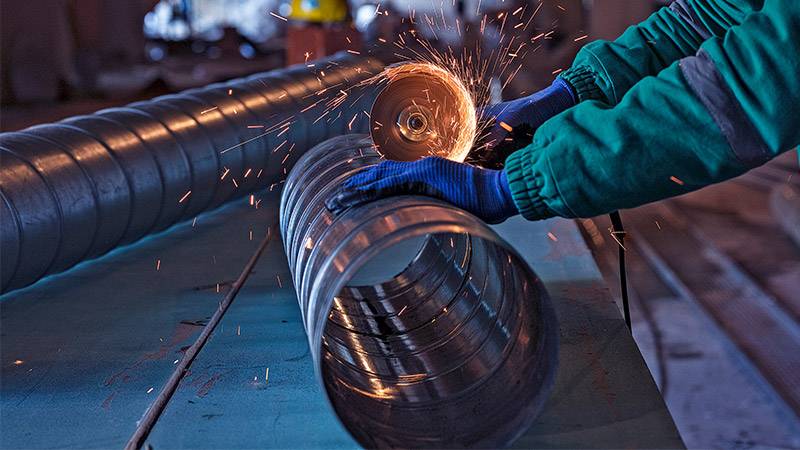
Cleveland-Cliffs, a prominent steel company in Ohio, has made remarkable strides in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The company’s efforts resulted in a nearly one-third reduction from its 2017 baseline, earning recognition from the Department of Energy as a 2023 Goal Achiever. This achievement is particularly notable given the steel industry’s reputation as a challenging sector to decarbonize due to its high heat requirements and continuous operations.
The steel industry, accounting for approximately 7% of global carbon dioxide emissions, plays a significant role in the fight against climate change. Companies like Cliffs are leading the way in adopting more sustainable practices. The demand for steel is expected to grow, especially for low-carbon steel, as the world transitions to renewable energy and aims to mitigate the impacts of climate change.
Innovative technologies have been central to Cliffs’ success. The company’s direct reduction plant in Toledo, opened in 2020, employs a lower-carbon method to process iron ore. This method involves using reformed methane, a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen, to remove oxygen from the ore. The resultant hot briquetted iron, an output of this process, can then be used in electric arc furnaces, which are increasingly used for recycling scrap steel.
Recycling steel through electric arc furnaces is a key strategy in reducing emissions. These furnaces can operate on electricity from renewable sources, thereby avoiding the carbon-intensive steps of refining iron ore. However, this method alone cannot meet all future steel demands or the requirements for certain high-grade steels.
The achievement and ongoing decarbonization efforts by Cliffs and other companies stand out because the steel industry has been seen as a hard-to-decarbonize sector, due to its need for high heat and continuous operations, as well as process reactions that emit more carbon dioxide.
In addition to direct reduction, Cliffs has made energy efficiency improvements across its operations. The company is also part of initiatives like the Midwest Alliance for Clean Hydrogen, exploring the use of hydrogen as a substitute for fossil fuels in steel production. This initiative could lead to significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions if successfully implemented.
The steel industry’s move towards renewable energy sources is evident in Cliffs’ agreement with EDP Renewables for wind power. Additionally, carbon capture technologies, while not yet proven in the steel industry, could offer another avenue for emissions reduction.
While Cliffs has been a leader in emission reduction efforts, the industry acknowledges the need for further advancements. According to Energy News, strategies like retiring coal-burning blast furnaces and increasing the use of renewable energy in electric arc furnaces are seen as essential steps for significant emission reductions.
The move towards green steel not only aligns with environmental goals but also has the potential to boost local economies by attracting businesses seeking clean energy sources. Companies like U.S. Steel have committed to net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050, illustrating a growing industry trend towards sustainable practices. Cliffs, while cautious in making such commitments, emphasizes a practical approach, focusing on achievable goals and immediate actions.
More inspiring green news similar to this: