Imagine growing your favorite herbs and veggies without soil, right in your kitchen. That’s the magic of hydroponics!
This innovative gardening method lets plants thrive in a water-based, nutrient-rich solution. As more people seek sustainable and space-saving ways to garden, hydroponics has become a popular choice.
Choosing the right type of hydroponic system can make all the difference.
Whether you’re a newbie or a seasoned gardener, understanding the different types can help you maximize your harvest. This blog dives deep into the various hydroponic systems available, shedding light on their benefits and how they work.
By the end, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge to choose the best system for your needs. Ready to embark on this green journey? Let’s get started!
What Are Hydroponic Systems?
Hydroponic systems are methods of growing plants without soil, using a nutrient-rich water solution. These systems provide plants with all the essential nutrients directly through water, ensuring they receive exactly what they need for optimal growth.
Maintaining nutrient balance in hydroponic systems is essential. Regularly monitor, analyze, and adjust the nutrient solution to ensure your plants receive proper nutrition, preventing imbalances that could hinder their growth.
Benefits of Hydroponic Systems
- Water Efficiency: Uses up to 90% less water than traditional soil gardening.
- Faster Plant Growth: Plants can grow up to 50% faster due to direct access to nutrients and oxygen.
- Space Savings: Ideal for small spaces, hydroponic systems can be set up vertically or in compact areas.
- Pest Control: Reduces the risk of soil-borne pests and diseases.
- Year-Round Gardening: Allows for continuous growth, regardless of the season.
Hydroponic systems are transforming how we grow food, making it more sustainable and efficient.
Wick System
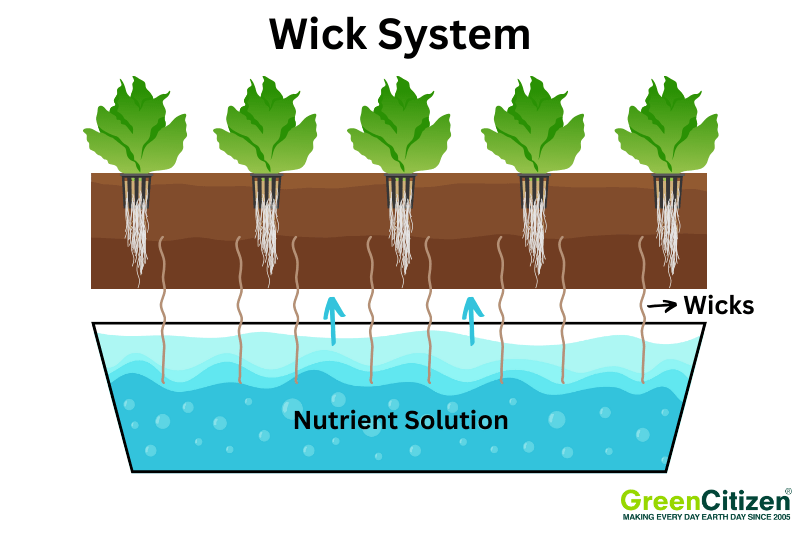
The wick system is one of the simplest types of hydroponic systems, making it perfect for beginners.
It works through capillary action, where a wick transports nutrient-rich water to the plant roots. Components include a container for the nutrient solution, wicks (often made from cotton or nylon), and a growing media like perlite or coconut coir. It supports plant growth and retains moisture and nutrients from the nutrient solution.
Here’s how it works: the wicks, placed in the nutrient solution, draw water up to the plant roots. The plants absorb the nutrients they need, ensuring steady growth.
Advantages
Disadvantages
- Simplicity: Easy to set up and maintain, no pumps or timers required.
- Cost-effective: Affordable materials and minimal maintenance costs.
- Beginner-friendly: Great for those new to hydroponics.
- Limited to Small Plants: Not suitable for larger plants that require more nutrients and water.
- Slow Nutrient Delivery: The wick system may not deliver nutrients as efficiently as other systems.
The wick system is like the training wheels of hydroponics. It’s ideal for small herbs or lettuce and offers a great introduction to the world of soil-free gardening.
However, for larger or more nutrient-demanding plants, you’ll need to explore other options.
Deep Water Culture (DWC)
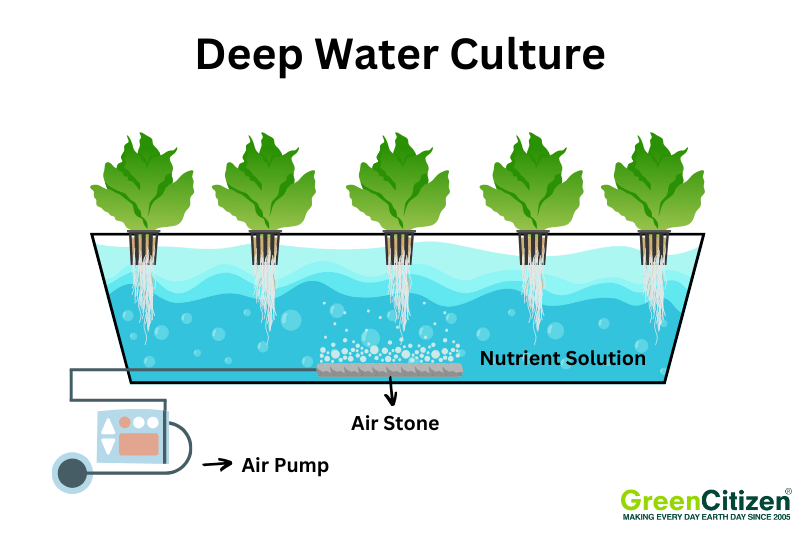
Deep Water Culture (DWC) is a popular hydroponic system where plants grow in net pots suspended in a nutrient-rich water solution. The roots dangle directly into the water, ensuring constant access to nutrients, water, and oxygen.
Using pure water free from chemicals is essential in DWC systems to prevent contaminants from affecting plant health.
Aeration is crucial in DWC systems. An air pump and air stone are used to oxygenate the water, preventing root rot and promoting healthy growth. Without proper aeration, plants can suffocate and die.
Advantages
Disadvantages
- Rapid Growth: Continuous access to nutrients and oxygen speeds up plant growth.
- Simple Setup: Easy to construct and maintain, making it ideal for beginners and hobbyists.
- Versatility: Suitable for various plants, from leafy greens to larger fruiting plants.
- Power Dependence: Requires a constant power supply to keep the air pump running.
- Temperature Control: Water temperature must be monitored to prevent overheating and algae growth.
- Maintenance: Regular cleaning is needed to prevent disease and nutrient buildup.
DWC is like a spa day for your plants, providing all the essentials for rapid and healthy growth. My first basil plant thrived in a DWC system, growing faster than I expected.
Just remember, keeping that air pump running is key to success.
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
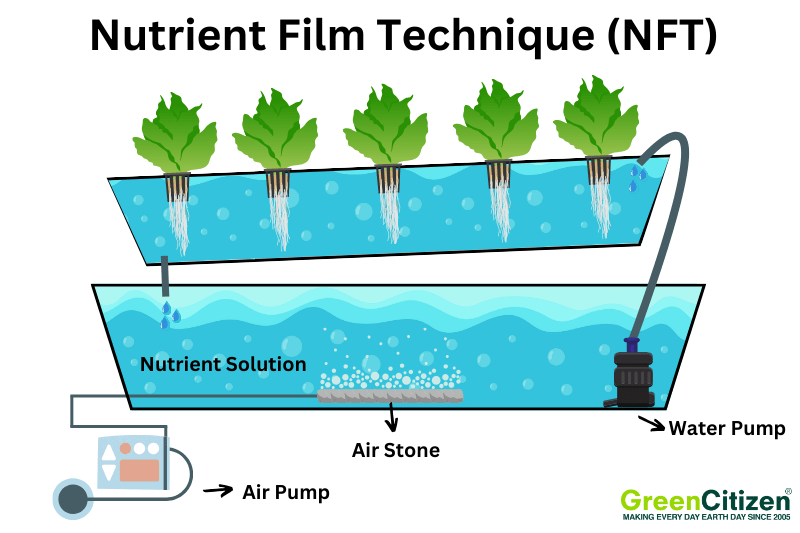
The Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) is a clever hydroponic system where a thin film of nutrient-rich solution continuously flows over the roots of plants. This setup requires a slight slope to ensure the solution moves smoothly through the channels, providing plants with a steady supply of nutrients and oxygen.
Plants use the green pigment chlorophyll to capture sunlight, which is essential for photosynthesis. This process allows them to split water molecules and produce carbohydrates.
In an NFT system, plants are placed in net pots along a sloped channel. The nutrient solution is pumped to the higher end and flows down, creating a shallow stream that nourishes the roots.
Excess solution collects at the bottom and is recirculated back to the top.
Advantages
Disadvantages
- Efficiency: Minimal water and nutrient usage, making it cost-effective.
- Excellent Oxygenation: Thin film allows roots to access plenty of oxygen.
- Space-Saving: Ideal for smaller plants and tight spaces.
- Greenhouse: NFT is the best system for starting your hydroponics greenhouse.
- Pump Dependency: If the pump fails, roots can dry out quickly, risking plant health.
- Clogging: Channels can become clogged with roots or debris, requiring regular maintenance.
NFT is like a plant highway, with nutrients and water flowing efficiently to where they’re needed most. My first lettuce crop in an NFT system grew beautifully, though I did have a minor scare when the pump clogged.
Keeping an eye on the system is essential, but the results are worth it!
Ebb and Flow (Flood and Drain)
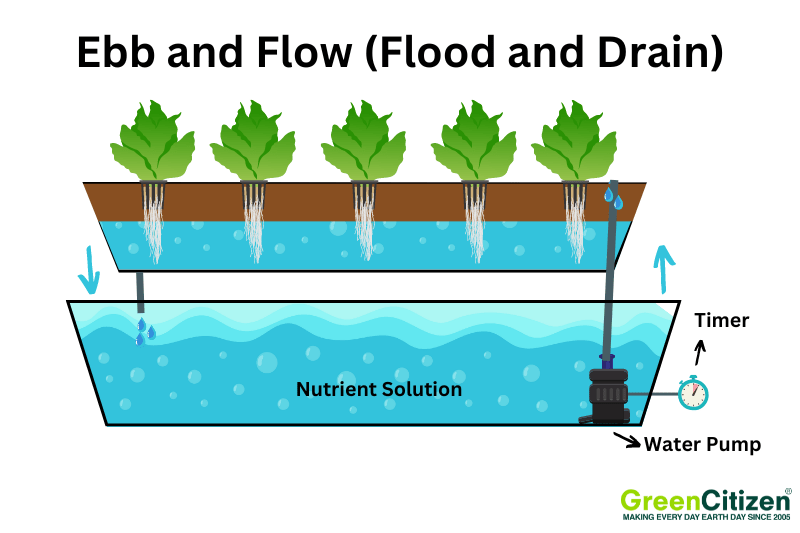
The Ebb and Flow system, also known as Flood and Drain, is a dynamic hydroponic method. It involves periodically flooding the grow tray with a nutrient-rich solution and then draining it back into a reservoir. This cycle provides plants with nutrients, water, and oxygen at regular intervals.
The green pigment present in plant leaves, known as chlorophyll, captures sunlight and uses its energy to undergo photosynthesis, a crucial process for their growth.
Components of this system include a grow tray, a nutrient reservoir, a water pump, and a timer. The timer controls the pump, which floods the grow tray at set times. Once the tray is flooded, the pump turns off, allowing the solution to drain back into the reservoir.
Advantages
Disadvantages
- Versatile: Suitable for various plant sizes and types.
- Effective Oxygenation: The draining process exposes roots to oxygen, promoting healthy growth.
- Nutrient Distribution: Ensures even nutrient distribution to all plants.
- Root Rot Risk: Overwatering or inadequate draining can lead to root rot.
- Maintenance: Regular cleaning and monitoring of the system are necessary to prevent clogs and failures.
Ebb and Flow is like giving your plants a refreshing bath and letting them bask in the air. My tomato plants thrived in this system, growing robust and healthy. Just be vigilant about the water cycles to avoid any root issues, and you’ll enjoy great results!
Drip System
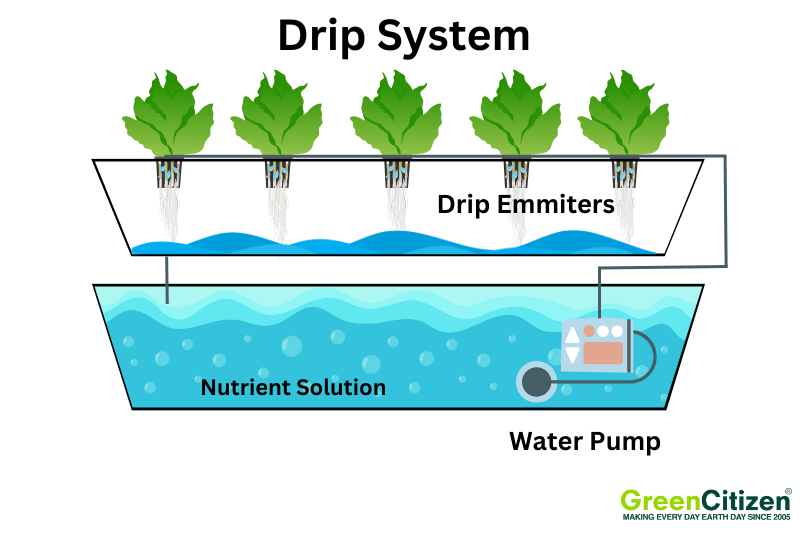
The drip system is a popular and versatile hydroponic method where nutrient solution is dripped directly onto the base of each plant. It ensures precise nutrient delivery and efficient water usage. There are two main variations: recovery and non-recovery systems.
In a recovery system, excess nutrient solution is collected and reused. This method is cost-effective and reduces waste. On the other hand, non-recovery systems do not recirculate the solution, which means less maintenance but higher nutrient costs.
Advantages
Disadvantages
- Precision: Delivers nutrients directly to each plant, ensuring uniform growth.
- Flexibility: Suitable for various plant types and sizes.
- Efficiency: Can be automated for consistent feeding schedules.
- Clogging: Drip emitters can clog over time, requiring regular inspection and cleaning.
- Monitoring: Requires careful monitoring of nutrient levels to prevent imbalances.
Drip systems are like giving your plants an IV drip, providing a steady supply of nutrients. I found my strawberry plants flourished with a drip system, yielding juicy and abundant fruits.
Just remember to check the emitters regularly, and you’ll enjoy a bountiful harvest with minimal fuss!
Aeroponics
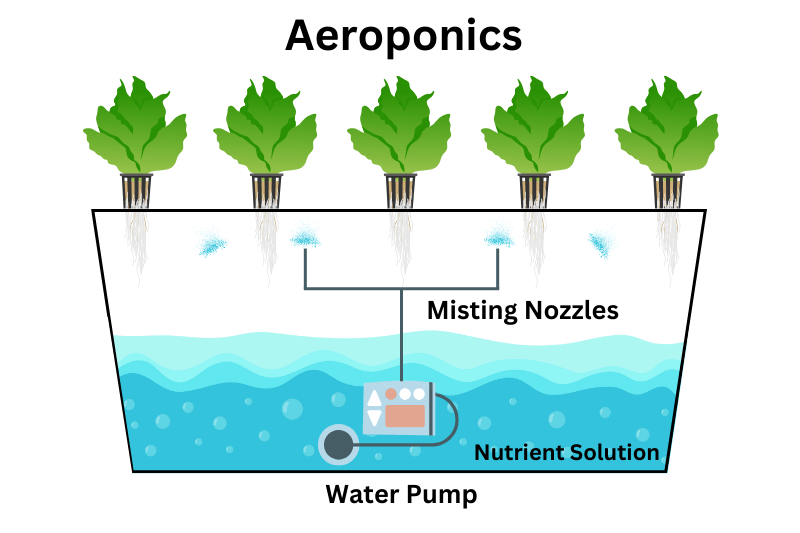
Aeroponics is the high-tech marvel of hydroponic systems. In this advanced method, plant roots are suspended in the air and misted with a nutrient-rich solution.
This ensures the roots have access to ample oxygen and nutrients, promoting rapid and healthy growth.
Advantages
Disadvantages
- Faster Growth: Plants grow significantly faster due to high oxygen levels around the roots.
- Efficient Nutrient Use: Nutrient solution is used sparingly, reducing waste.
- Space-Saving: Ideal for vertical farming and maximizing space.
- Complicated: Complex and require precise control over misting intervals and nutrient concentrations.
- Monitoring: They can be more expensive to set up and maintain compared to other systems.
Aeroponics is like sending your plants to a spa, where they get misted with nutrients and air, ensuring they thrive. My first try with aeroponics was a bit daunting due to its complexity, but the results were impressive.
Just be prepared for a higher initial investment and the need for careful monitoring to keep everything running smoothly.
These days, aquaponics systems are also getting popular.
Choosing the Type of Hydroponic Systems
Selecting the right hydroponic system can seem daunting, but it doesn’t have to be. The best system for you depends on several factors, including space, budget, plant types, and experience level.
- Space: If you have limited space, consider vertical systems like the Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) or aeroponics. For more extensive setups, Deep Water Culture (DWC) or Ebb and Flow systems work well.
- Budget: The Wick system and Drip systems (especially recovery types) are budget-friendly options. Aeroponics, while efficient, can be costly due to its high-tech nature.
- Plant Types: Smaller plants like herbs and lettuce thrive in Wick and NFT systems. For larger plants, look at DWC or Ebb and Flow systems, which can handle their greater nutrient needs.
- Experience Level: Beginners might find the simplicity of the Wick system appealing. More experienced growers can explore advanced options like aeroponics for greater yields.
Things I Learned the Hard Way
- Start simple and scale up as you gain experience, especially regarding hydroponics maintenance.
- Consider maintenance needs; some systems require more upkeep than others.
- Factor in the climate; some systems need specific temperature and humidity levels.
When I started, I chose the Wick system for its simplicity, then moved to DWC as I gained confidence. Remember, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution—choose what fits your needs best, and enjoy the journey!
Some Personal Tips
Starting with hydroponic gardening can be a fun and rewarding experience. Here are some practical tips to help you succeed:
Regular Maintenance: Check your system daily. Ensure pumps, timers, and aerators are functioning properly. Regular cleaning prevents algae and mineral buildup.
Monitor Nutrient Levels: Use a quality nutrient solution and monitor its levels. Invest in a pH and EC meter to ensure your plants get the right balance of nutrients.
Watch the Water Temperature: Keep water between 65-75°F (18-24°C). Too hot, and your plants might suffer; too cold, and growth can slow down.
Troubleshooting Common Issues:
- Yellowing Leaves: This often indicates nutrient deficiencies. Check your solution's pH and nutrient levels.
- Root Rot: Ensure proper aeration and avoid overwatering. Regularly check for signs of decay.
- Slow Growth: Sometimes, it's the light. Ensure your plants get adequate light, ideally 12-16 hours a day.
I once had a bout of yellowing leaves in my basil plants. Adjusting the pH and adding a bit more nutrient solution turned things around quickly.
Don’t be afraid to experiment and learn from your plants.
Hydroponics is a journey of continuous learning. Stay patient, observe closely, and enjoy the process of watching your plants thrive!
