LEED Reporting: Solid Waste Management
The following article addresses an initiative called Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED).

LEED: Solid Waste Management and Electronic Waste
While this program serves primarily as a green incentive for building managers, owners, and developers, everyone can benefit from a neighborhood, city, or metro area populated with green buildings. Read more to learn about what LEED does, why GreenCitizen supports it, and why you should be excited about it.
What is Electronic Waste?
Electronic waste (e-waste) is categorized as any electronic equipment that is near or at the end of its useful life. If it plugs into a wall or has batteries, it will one day be e-waste. E-waste is the quickest-growing source of waste in developed nations. When not disposed of properly, it can have serious health impacts, such as toxic chemicals leaching from landfills into groundwater systems. Harmful Effects
California’s Electronic Waste Recycling Act, along with various federal and local statutes, makes it illegal to discard your end-of-life electronic equipment in the same way that you’d dispose of other solid waste. CalRecycle (formerly the California Integrated Waste Management Board) operates this program to encourage the “three R’s” of good environmental stewardship: Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle. Property managers with a solid waste management plan for e-waste can avoid the legal penalties imposed for dumping these electronics while eliminating the cost of storing or disposing of end-of-life devices. Additionally, you’ll know that your e-waste isn’t ending up in landfill and that you’re doing your part to help the planet.
What is LEED?
Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED), an initiative by the U.S. Green Building Council is a worldwide green building rating system that provides a framework to create healthy, highly efficient, and cost-saving buildings. E-waste is considered a subset of solid waste management, which is one of the metrics for determining the environmental sustainability of a property or building — and one of the major reasons why GreenCitizen is interested in this initiative.

Why get a LEED certification?
If you’re a property manager, a building owner, or in the construction industry, LEED certification is in your best interest. As well as saving resources and generating less waste, LEED buildings attract tenants, cost less to operate, and boost employee productivity and retention.
Here are a few of the benefits:
- Reduced operations costs - One study found that green buildings showed a decrease in operating costs -15% for new construction and 13% for retrofits — over a five-year period, with payback times of eight and seven years respectively.
- Higher rents - Many companies will pay more to occupy green properties. LEED-certified units were found to command a rent premium of 9.1%, versus 4.7% for non-certified green properties over market average.
- Lower vacancy and turnover rates - Green-certified buildings tend to be located in walkable neighborhoods and are more comfortable than conventional buildings because of their superior weatherization, lighting, and ventilation requirements. This means that tenants are more likely to renew their lease.
- Quality assurance - Green-certified construction means that everything is up to code. Not only will this ensure that the building will perform as expected, but it also reduces the likelihood of ongoing maintenance issues that can plague managers of non-certified buildings.
- Heightened interest from investors - LEED certification offers proof that a building is up to code, ensures that the building will perform as expected, and reduces the likelihood of ongoing maintenance issues.
- Financial incentives - The possibility of easier financing, lowered insurance premiums, and grants and loans can significantly reduce the real cost of construction and maintenance of green-certified buildings.
How does it work?
The LEED rating system is based on earning credits that have a point value. Certification requires a minimum number of points. It’s possible to get credits for recycling activities, such as solid waste management. There are four different levels of LEED Certification, each requiring an increasing number of points:
| LEED Certification Level | Points Required |
|---|---|
| LEED Certified | 40-49 |
| LEED Silver | 50-59 |
| LEED Gold | 60-79 |
| LEED Platinum | 80+ |
How do I Earn Points?
It’s possible to earn two points from proper ongoing solid waste management if the building hits the performance measures for both durable goods and ongoing consumable waste (see below for how these are defined). This involves maintaining a waste reduction and recycling program that reuses, recycles, or composts the following:
- Atleast 50% of ongoing consumables (by weight or volume)
- Atleast 75% of the durable goods waste (by weight, volume, or replacement value)
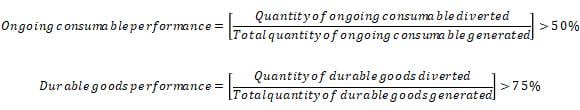
- Additionally, safely dispose of all discarded batteries and mercury-containing lamps.
- Required to provide clearly labeled battery collection bins in high-visibility areas. Identify a qualified, licensed recycler that will recycle the batteries in accordance with state and federal requirements.
- 100% of mercury-containing lamps to be safely disposed. Establish procedures for handling broken lamps, and have a designated space for storing used lamps before they’re collected for recycling.
It is also possible to earn one extra point for exemplary performance by achieving a higher performance score. This would require a 75% of ongoing consumables performance and a 100% durable goods performance.
What Are Ongoing Consumables and Durable Goods?
Ongoing Consumable: A product that has a low-cost unit and is regularly used and replaced in the course of business. Examples include
paper, toner cartridges, binders, batteries, and desk accessories.
Durable goods: Products with a useful life of two or more years before and a likelihood of infrequent replacement. Examples include furniture, office equipment, appliances, external power adaptors, televisions, and audiovisual equipment.
How Do I Apply?
- Register your project by completing the key forms and submitting payment.
- Apply for LEED certification by submitting your completed application and paying a review fee.
- The Green Business Certification Inc. reviews your LEED application.
- Receive the certification decision.
How Long Does Certification Take?
Your eligibility will be measured in a period of between 3 and 24 months. Note that all performance periods for certification must end within the same 30-day interval and that the application must be sent within 60 days of the final performance period. Following the first certification, projects must recertify within five years. The project is eligible for recertification as often as every 12 months. The performance period then runs from last certification until recertification. As solid waste management is ongoing, the project should always continue to track its performance after being certified.
Written By Nicholas Yeh