Meat is king!
30% of the calories consumed by people around the world are of meat origin.
In the US, 225 pounds of meat was consumed per capita in 2020. This is a new record and a huge leap compared to, let’s say, 1960 when the number was 167 pounds.
Nowadays, new ways of meeting the global meat demand are emerging.
It’s time to ask yourself this: would you eat lab-grown meat?
Here’s the ultimate guide on the best meat alternatives and substitutes and why we should consider them.
What are Meat Alternatives?
There are several meat alternatives nowadays. These can be divided into three groups:
Traditional Substitutes
Vegans and vegetarians will be well-acquainted with these. Traditional substitutes include tofu, kidney beans, seitan, jackfruit, and more. Some of the most common traditional ingredients in meat substitutes include wheat and soy proteins, grains, beans, wheat gluten, and pea proteins.
Plant-Based Meat Alternatives
The meat industry is currently facing numerous challenges, such as business, ethical, and most importantly, environmental.
On the other hand, startups that use technology to produce plant-based meat, are flourishing.
One of such examples is Beyond Meat, which produces a plant-based Beyond Burger. Beyond Meat’s revenue was $470M in 2020 only, and they’re continuing to expand. In 2021 they announced partnerships with McDonald’s and Yum! Brands.
Beyond Meat isn’t the only example of success in making plant-based meat alternatives.
Impossible Foods has also seen huge growth recently. They have partnerships with Starbucks and Trader Joe’s, among others.
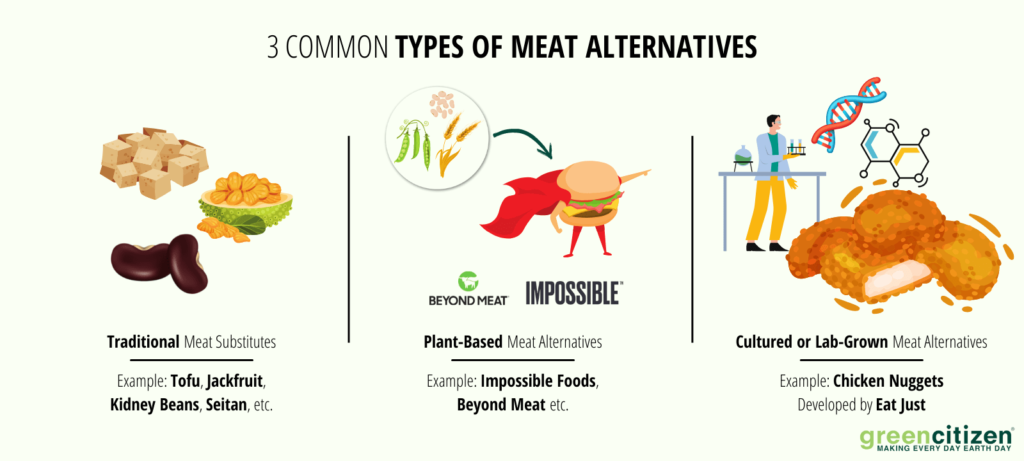
Cultured or Lab-Grown Meat Alternatives
The final meat alternative is cultured or lab-grown meat. This meat has both environmental and ethical benefits.
A US company, Eat Just, started selling their lab-grown chicken nuggets to Singapore consumers in December 2020. This meat is grown from cells in a lab. Eat Just uses bioreactors that are adapted from pharmaceutical companies. So far, they’ve been successful. In April, Eat Just partnered with a restaurant, which sold out all the lab-grown meat servings for the day in a matter of minutes.
However, cultured or no-kill meat is facing some challenges. Namely, the production cost is high, and not everyone will want meat produced in this way.
Meat and seafood production is expected to double to 1.2 trillion pounds by 2050. The Earth can’t supply enough water, fertilizers, and fuel that the animal industry requires.
What Is the Significance of Meat Alternatives? Is There Any Environmental Benefit?
Right now, about 30% of Earth’s land is used for livestock farming. The demand for meat is expected to double by 2050, and humanity will struggle to meet this demand.
The future of meat is divided into two paths:
- Traditionally produced meat which comes from cows fattened on corn
- Meat grown in the lab from yeast and modified to resemble the traditional meat taste.

Read More:
Here’s the importance of both and how they impact our environment.
Farm Factories
To understand why alt meat is significant, you have to be familiar with the current farming conditions.
Let’s go to Garden City, Kansas. This is the birthplace of CAFOs (Concentrated Animal Feeding Operation). Another name for this is a factory farm.
Factory farms put a large number of cows in a small area to maximize the land profit.
Once cows reach the required weight, they’re moved to feedlots, where they are fed on corn, protein supplements, and antibiotics until they reach 1,100lbs, when they are slaughtered.
Yes, animal cruelty is a concern here.
But, even more so, environmental issues are staggering.
Environmental Impacts of Factory Farming
Here’re only a couple of issues that animals grown in farm factories cause:
The Pesticide Issue
Animals are fed crops grown through industrial farming. These crops are exposed to huge amounts of pesticide, which remains in the cattle bodies and is transferred to people when we eat their meat.
Where Does the Poop Go?
It’s proven that large factory farms produce more waste than some US cities. For example, 800,000 pigs will produce 1.6 million tons of waste.
For outdoor farms, this huge amount of waste piles up underneath the cattle, and once it rains, it goes into waterways and pollutes drinking water.
For indoor farms, the manure has to be scooped out. Because it can carry bacteria such as E. Coli, farmers won’t put it on their fields. Instead, they put it in holding ponds which tend to overflow when it rains.

Greenhouse Gas Emission
Because cows can’t stomach corn, belching and manure decomposition happens on a high level. Livestock accounts for 14.5% to 18% of the year’s GHG emissions in the world.
River and Groundwater Pollution
It’s estimated that cattle, hog, and chicken waste has polluted 35,000 miles of rivers in 22 states and groundwater in 17 states.
This is what plant-based meat is trying to replace.
The world population eats 130,000 animals per minute! 130 million chickens and 4 million pigs are slaughtered for meals daily.
Can Plant-Based Meat Solve the Environmental Issues?
The two main producers of plant-based meat are Beyond Meat and Impossible Foods.
These companies have spent years researching the hamburger taste and trying to translate that into plant-based alternatives.
They’ve discovered the main component — heme. Heme comes from root nodules of a soy plant. It makes a plant-based burger bleed and gives it a meaty flavor.
To be able to use heme protein, these companies genetically modified a yeast cell to produce heme for mass burger production.
So, these burgers aren’t so plant-based, as they are lab-based.
A report by Beyond Meat claims that their burger:
- Creates about 90% less greenhouse emissions
- Needs 46% less energy
- Has 99% less impact on water scarcity
- Almost 93% less impact on land use
Note: While these numbers look promising, it’s worth noting that this is a report done by Beyond Meat, the company behind the burger. Independent, third-party studies are needed to establish the true impact of plant-based meat production.
Plant-Based Meat vs. Cultured or Lab-Grown Meat: Understanding the Differences
We’re all familiar with vegan meat substitutes, such as veggie burgers.
But, do you know the differences between plant-based meat alternatives vs. lab-grown meat? Here are the most significant differences between the two.
Plant-Based Meat Alternatives
Plant-based meat is a term used to describe food that mimics meat products, but it’s made from plants.
However, there are differences in plant-based meat alternatives. Vegans stay clear of all animal products, which include eggs and dairy.
Vegetarians usually don’t eat meat but aren’t so strict with their diet.
If you fall under one of these two groups, keep this in mind because vegetarian meat can still have ingredients that vegans won’t consume.
A plant-based burger that you buy at a supermarket can only be made of mushrooms and beans or contain pea protein and soy to give it that authentic meat texture.
Some ingredients that are used to make plant-based meat include:
- Seitan
- Wheat gluten
- Coconut oil
- Pea protein
- Beans
- Tofu
- Soy
- Vegetables
So, is plant-based meat healthy?
Yes, it is. Several studies show that swapping meat for plants can have lowered diabetes risk, lower chances of cancer and heart disease.
Compared to cattle, plants need fewer environmental sources — namely, less water and space, which helps battle climate change.
Cultured or Lab-Grown Meat
Lab-grown meat, also known as cultured meat, is produced from animal cells in a lab.
For example, a cow is put under local anesthesia, and a small muscle sample is taken to make beef.
Then this muscle is cut into small pieces to release the stem cells. The stem cells are put in a bioreactor, where they are immersed in a broth. This environment helps the cells multiply. Then the stem cells become muscle fibers that bunch together. After several weeks the meat is ready for consumption.
So, how nutritional is alt meat?
It’s packed with protein, and it can also contain fat. What’s more, because this fake meat is lab-made, the fat content can be controlled. There’s not a big difference between nutritional levels of alternative and real meat.
However, there’s still the risk of eating too much meat. This can lead to cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and even cancer.
On the other hand, eating plant-based meat won’t cause any of these. So, plant-based is the healthier option.
What about the environmental impact lab-grown meat has?
Well, the situation isn’t great either.
Several studies published in 2019 found that lab-grown meat can generate even bigger concentrations of CO2 over time. CO2 takes longer to dissipate than the methane the cows produce. There’s a possibility that these emissions could be reduced in the future if the right production efficiency is achieved.
However, plant-based meat also takes this round, as it’s better for the environment than cultured meat.
You would save more water by not eating one pound of meat than not showering for six months.
Are Meat Alternatives Good for Our Health?
I’ve mentioned how plant-based meat is good for us. It can contain antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals. All of these have health benefits.
Research also states that a plant-based diet is good for weight management and can prevent various health issues.
The World Health Organization (WHO) warns about the dangers of red meat, such as carcinogens, which can increase the chances of cancer. On the other hand, the American Heart Association (AHA) says that plant protein improves heart health.
But, it doesn’t mean that plant-based products aren’t without cons either. They can contain fillers and sodium and lack Vitamin B12, which is essential for the body.
What about the nutritional value of cultured meat?
It’s certainly safer than conventional meat. It’s made in a protected environment researchers control. On the other hand, traditional meat is part of an animal that’s in contact with the world and can get infected.
We can conclude that cultured meat isn’t at risk of encountering E. Coli or salmonella, which kill millions of people around the world each year.
However, cultured meat is still a relatively new product, and we don’t know its consequences.
The fact is, unexpected biological mechanisms may always occur, and scientists are people too. They make mistakes just like everyone else.
60% of all mammals on Earth are livestock, 36% are humans, and 4% are wild!
Okay, You Got Me (!) But How Do They Taste?
I’ve talked about the environmental impact and the nutritional value of these meats. But, the crucial question for possible consumers is: how do alternative meats taste? Good alternative meat should mimic the smell, texture, and taste of the real thing.
How Does Plant-Based Meat Taste?
We’ve seen significant improvements over the years in vegan and vegetarian patties you can find at the supermarket. While it depends on the manufacturer, nowadays, these mostly taste like real meat, especially when cooked and topped.
In Sweden, Burger King released a plant-based Rebel Whopper. They didn’t tell the customers which meat they’re eating, but they could find out on the app once they had the burger. 44% of customers couldn’t tell the difference.
How Does Lab-Grown Meat Taste
But what about cultured meat?
The first lab-grown beef burger was presented in London in 2013. The taste was underwhelming. It was reportedly dry and dense. This was likely because it has only muscle fibers and no fat.
Beef fat melts slowly over a wide temperature range. The slow release of fat makes the beef juice.
Luckily, there have been huge improvements since then. Nowadays, some companies claim to be able to reprogram stem cells into fat or muscle, so they can grow together, just like they would in an animal.
This means the flavor is just the same. Moreover, different species cells can be grown together, and we can have completely new flavors.
10 Best Meat Alternatives You Can Taste Right Now!
I’ve personally tested countless meat alternative versions. This is my list of the ten best fake meats out there.
Beyond Meat: Rethinking Protein for a Greener Planet

Beyond Meat has become synonymous with the plant-based revolution — and for good reason. This brand isn’t just selling meat alternatives; it’s rewriting the protein playbook by offering products that look, cook, and satisfy like meat but come with a fraction of the environmental cost.
At the core of Beyond Meat’s mission is sustainability. Their flagship items — like the Beyond Burger and Beyond Sausage — use pea protein, beet juice, and other plant-derived ingredients to create realistic textures and flavors without relying on animal agriculture, which is notoriously resource-intensive. According to their own life cycle analysis, Beyond Meat products generate 90% fewer greenhouse gas emissions than beef, use 99% less water, and require 93% less land.
The company is also transparent about its goals, publishing climate impact data and pushing toward a fully regenerative supply chain. Beyond Meat even avoids GMOs and uses recyclable packaging whenever possible, doubling down on ethical sourcing and manufacturing.
For consumers looking to reduce their meat consumption without compromising on taste or texture, Beyond Meat is setting a gold standard for plant-based innovation.
Impossible Foods: Bold Flavor, Smart Science, Big Impact

Impossible Foods isn’t afraid to wear its science on its sleeve. This Silicon Valley-based brand has flipped the script on meat alternatives by engineering plant-based products that mimic meat down to the molecular level. The key? Heme — the iron-containing compound that gives their burgers that meaty flavor and juiciness.
But it’s not just lab smarts that make Impossible Foods a sustainability leader. The company’s mission is crystal clear: eliminate the need for animal agriculture. And their approach is paying off — their burger uses 87% less water, produces 89% fewer emissions, and requires 96% less land compared to traditional beef.
Impossible also scores high in ingredient transparency and product development ethics. Their sourcing strategy prioritizes non-GMO soy, and they rigorously evaluate water, land, and energy inputs at every stage. The company continuously updates its environmental reports and remains outspoken about replacing livestock with plants to fight climate change.
In the meatless aisle, Impossible Foods delivers more than a burger — they offer a glimpse into a scalable, science-driven food future.
Dr. Praeger’s: Clean Ingredients with a Health-First Philosophy

Dr. Praeger’s may not boast the flashy marketing of some newer brands, but this family-run company has quietly built a legacy rooted in clean eating and conscious living. Since 1994, they’ve focused on creating veggie-forward meals with recognizable, whole-food ingredients — a refreshing take in a sea of heavily processed alternatives.
Sustainability at Dr. Praeger’s starts with simplicity. Their products — like the California Veggie Burger — often feature short ingredient lists, spotlighting real vegetables, legumes, and grains. There’s no soy protein isolate or mystery additives here — just food that supports both personal health and planetary wellness.
The brand leans into responsible sourcing, avoiding GMOs, artificial preservatives, and unnecessary fillers. Their facility in New Jersey is also making strides toward energy efficiency and waste reduction.
If your version of a meatless diet leans more “plant-packed” than “lab-cooked,” Dr. Praeger’s offers a back-to-basics approach that doesn’t sacrifice flavor — or ethics.
Wholesome Provisions: High-Protein, Low-Impact Fuel for the Future

Wholesome Provisions is the go-to brand for health-conscious consumers who want more from their plant-based meals — more protein, more convenience, and less environmental baggage. While the packaging leans clinical, the mission is anything but sterile: to create nutrient-dense, meat-free meals that support wellness and sustainable living.
Their products, like the popular plant-based meatless crumbles, are built around soy and pea protein — offering high protein counts without the cholesterol, saturated fat, or resource drain of animal agriculture. With low net carbs and gluten-free options, Wholesome Provisions caters to diverse dietary needs while championing a cleaner food system.
On the sustainability front, the brand favors streamlined ingredient sourcing and minimal packaging waste, and many of their products are shelf-stable — cutting back on energy-intensive refrigeration and food waste.
While they’re not a household name just yet, Wholesome Provisions is proving that eco-friendly eating can be as practical as it is nutritious.
Gardein: Meat-Free Meals Made for Everyone

Gardein has long been a supermarket staple for vegans, vegetarians, and flexitarians alike — and for good reason. This Canadian-born brand has built a loyal following by delivering a massive variety of plant-based comfort foods that don’t skimp on taste or texture. Think meatless meatballs, crispy tenders, and fishless filets — all crafted with the environment in mind.
What makes Gardein stand out is its commitment to scalable sustainability. Their meat alternatives use significantly less water, land, and energy than conventional meat, and the brand is vocal about reducing global meat consumption to fight climate change.
Gardein is part of Conagra Brands, which has pledged to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and source 100% renewable electricity by 2030. Gardein’s product line is mostly non-GMO and plant-forward, with a mix of soy, wheat, and ancient grains that support biodiversity in agriculture.
Whether you’re easing into meatless Mondays or going fully vegan, Gardein offers a guilt-free gateway to sustainable eating.
Native Forest: The Plant-Based Pantry Hero

While best known for their organic coconut milk, Native Forest offers a full line of plant-based pantry staples that make sustainable cooking easier and tastier. As part of Edward & Sons Trading Co., the brand is steeped in organic, non-GMO, and fair-trade principles — making them a quiet but powerful player in the meat alternatives world.
Native Forest is serious about ecological responsibility. Their coconut products are sourced from sustainably harvested trees, supporting reforestation and minimizing harm to wildlife habitats. The brand also uses BPA-free, recyclable cans and avoids chemical preservatives and artificial flavorings.
Beyond coconut, they offer jackfruit products — a popular whole-food meat substitute that’s perfect for pulled “pork” or tacos — all grown using ethical labor and regenerative farming methods.
In an industry often dominated by lab-made meat replicas, Native Forest reminds us that whole foods can be just as meaty — and even more sustainable.
Lightlife: A Legacy of Clean, Conscious Plant-Based Eating

Lightlife has been in the meatless game since before it was cool — founded in 1979 with a vision of making plant-based eating accessible to everyone. Today, they’re one of the most recognized names in the space, offering everything from plant-based hot dogs to tempeh and burgers.
But what really sets Lightlife apart is their focus on transparency and simplicity. In 2019, they famously took out a full-page ad calling out competitors for using overly complex, synthetic ingredients. Their commitment? Keep it clean, keep it honest. Most of their products have fewer than 10 ingredients, and all are non-GMO, vegan, and soy-based.
From a sustainability standpoint, Lightlife operates a carbon-neutral production facility and uses recyclable packaging. They’re also working on reducing water and energy usage across the supply chain. Their parent company, Greenleaf Foods, is helping scale their impact without compromising on ethical sourcing and product integrity.
For plant-curious eaters who want real ingredients and real impact, Lightlife brings legacy, leadership, and a lighter footprint.
Why Are Meat Alternatives More Expensive Than Real Meat?
Plant-based meat needs less grains, energy, and water compared to traditional meat production.
So, why is it more expensive?
It’s because meatless alternatives have smaller-scale productions, while beef production is done on a larger scale and can ensure the products are affordable.
Another reason why meat alternatives are more expensive is that the manufacturers operate in a free market.
Both Beyond and Impossible are unable to meet the current demand. If they lowered their prices, it would mean lower revenue, which will hurt their ability to go bigger and meet the demand.
While the vegan market is growing by leaps and bounds, it still remains small, especially compared to the traditional meat market.
Because of this, it’s more difficult for companies to negotiate a lower price for their ingredients, such as peas and soybeans.
The production of lab-grown meat is also currently expensive because the process is restricted to small-scale operations in labs.
Meat production accounts for 40% of global habitable land and 15% of gas emissions.
The Hopeful Future of Meat Alternatives
Meat consumers have been growing more conscious about what they eat and how this is affecting the environment.
The alternative food sector in the US grew 27% in 2020, and 71 million households bought meatless meat.
So, how are meat producers reacting to this?
Producers of real meat are worried about the effect of plant-based meat alternatives on their business. Some have even filed lawsuits to prevent alt meat manufacturers from using the word meat on their products.
Others are realizing the value and potential of the alt meat industry and are starting to invest in it. Nestle plans to invest $100 million in a plant-based factory in China.
The good news is that plant-based meat manufacturers are planning to lower the prices.
At the beginning of 2021, both Beyond and Impossible stated their plans to lower the prices. They plan to achieve this by having more manufacturing plants and finding ways to optimize production.
Impossible even stated they will have 15% lower prices.
What about cultured meat?
It’s also going to impact the market. While the prices of lab-grown meat are currently high, this is likely to decrease in the future considerably.
Then, it’s a matter of which company will get their lab-grown meat on the market first.
As technology and genetic engineering advance, we will see lab-grown and plant-based meat innovations in taste, flavor, and healthiness. These will incentivize consumption.
Meat Alternatives and Substitutes: Final Thoughts
If you’ve come this far, congratulations! You’re now an expert on all substitutions for meat.
The fact of the matter is, the world’s population is growing rapidly, and meat demand is increasing along with it.
Soon, we won’t be able to meet it.
Replacing one industry with another is never a good solution. Instead, we should combine all of these: traditional meat substitutes, plant-based meat, and lab-grown meat.
If one of these doesn’t work for you, try another option. You’ll be surprised how varied the meat alternatives industry is. You’re guaranteed to find alt meat that’ll work for you.
Finally, do your own research and taste test. Switching to alt meat even for one meal a day will make a huge difference.

