Solar panels are commonly found on rooftops and across the countryside. They power our RV trailers, boats, and off-grid cabins. Hikers even strap portable solar panels to their backpacks and charge their gadgets on the go.
But how do solar panels work? Can they work at night and on cloudy days? Let me share my knowledge as an electrical engineer and a solar homeowner.
Solar panels convert the energy of the sun into electrical energy using a process known as the photovoltaic effect. The photovoltaic effect is an electrochemical process in which solar cells transform sunlight into electric current by putting free electrons in motion. The flow of these free electrons becomes the electrical current that solar panels capture.
But this is a low-voltage direct current, like the one in your car battery, while most appliances in your home use high-voltage alternating current.
This means there are still a few more steps before we can use this electricity to power our homes and appliances.
What Is the Photovoltaic Effect and How Does It Work?
The photovoltaic effect is a process in which sunlight particles called photons energize free electrons, which are then “directed” to become electrical current, as shown on this solar panel work diagram.
The process takes place in solar cells, which are no thicker than a human hair.
Each solar cell is made of two slices of semiconductor material, most often silicon, that is specially treated to create a negative and a positive plate.
We need a negative and a positive charge to create an electric field that directs free electrons and effectively creates a flowing current.
Much like magnetic fields are created between the (+) and (-) poles, electric fields in solar cells are created when one semiconductor plate has more free electrons and the other plate has fewer.
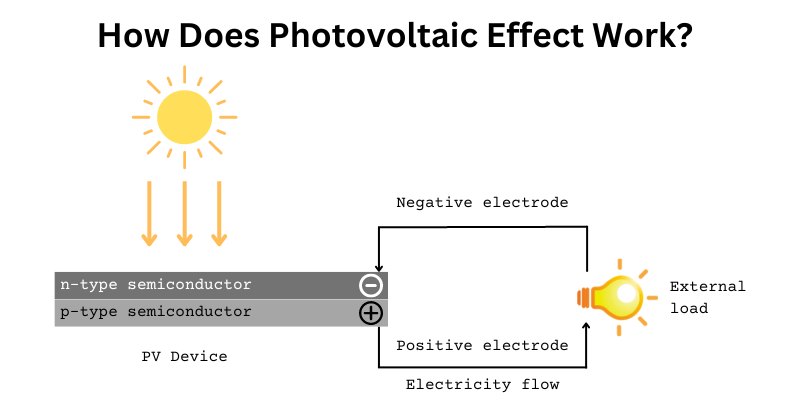
To make this possible, one plate is doped with phosphorus which has more electrons (negative particles) than silicon — this is the negative charge, while the other plate is doped with boron, which has fewer electrons than silicon — to give it a positive charge.
As sunlight particles knock electrons free, the electric field pushes them in one direction.
Each solar cell has metal plates on its sides that collect these electrons and transfer them to wires like any source of electricity.
The process is the same for both monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar panels.
How Do Solar Panels Work and Power Your Appliances?
Now when we explain how the photovoltaic effect works, let’s take a look at how solar panels create electricity to power our appliances.
1. Sunlight activates the panels
Each solar panel consists of a layer of solar cells protected by a glass panel, a metal frame, and wiring. Solar cells, also known as photovoltaic cells, are activated by sunlight during daylight hours.
2. Cells produce electric current
Each solar cell consists of a thin semiconductor plate made from two layers of silicon. One layer is positively charged, and the other has a negative charge, so they form an electric field.
When sunlight particles reach a photovoltaic solar cell, they knock electrons loose from atoms of the semiconductor material. These loose electrons are directed by the electric field created by two layers, and they become an electrical current.
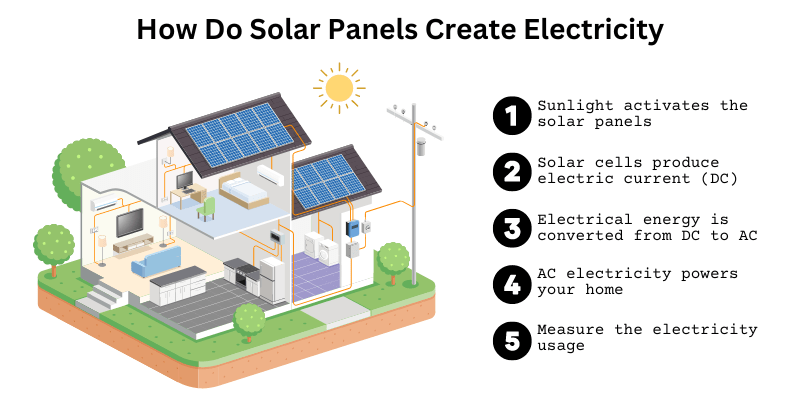
3. Electrical energy is converted from DC to AC
The electricity that solar panels generate this way is direct current (DC) electricity which is not the type of electricity that powers most appliances. We need alternating current (AC) electricity. So to convert DC electricity into AC electricity, you need a device called an inverter.
Today you can find inverters that are configured as one inverter unit for the entire system or as individual microinverters attached to the back of each panel.
4. AC electricity powers your home
When the solar panel electricity has been converted from DC to AC, it runs through your electrical panel and is distributed within your home through wall sockets to power your appliances. At this point, this AC electricity is no different from the electrical energy generated in power plants and distributed through the grid by your electric utility company.
You don’t have to change anything inside your home to use solar energy. And since you are still connected to grid power, you can always draw extra power from the grid to make up for the solar shortages.
5. Measure the usage
On cloudy days, and overnight, your solar panel won’t be able to capture enough sunlight to use for energy. On the other hand, in the middle of the day, when nobody is likely home, they may collect much more energy than you need to operate your home.
This is why you want to use a meter to measure the electricity flowing in both directions — to and from your home. Your utility company may offer credits for any surplus energy you send back to the grid. This is called net metering.
Alternatively, you can hook your solar panels to a solar battery and store the generated energy for times of day when the solar output doesn’t meet your home’s demand.
Do Solar Panels Work At Night?
Solar panels don’t work at night. At least not in the photovoltaic sense, as solar cells must have sunlight to create electricity.
And this has been one of the biggest challenges of the solar movement.
If solar panels can’t produce power at night, how can we hope they can replace fossil fuel power plants?
What is more, solar energy is considered one of the best ways to provide power to some of the most disadvantaged communities in the world, such as those in sub-Saharan Africa, where 44% of the population has no access to electricity.
The good news is that scientists and solar engineers are not wasting time.
Currently, they are developing solar panels that offer two indirect ways to produce energy overnight.

So how do solar panels work at night?
There are two main technologies: using thermal cooling and rain.
This innovative solar panel works on a simple principle that materials exposed to the sun during the day have to cool off at night.
As these solar panels cool at night, they generate electricity from the temperature difference between the cooler panels and still-warm surrounding air.
This is done using a thermoelectric generator, which produces power as heat passes through it.
This thermoelectric generator also boosts output from solar panels during the day, by running in reverse — it produces extra electricity as the panels heat up.
Apart from sunset, heavy clouds and rain can also make solar panels less effective. However, scientists have a solution for that as well.
They have designed a solar panel that creates electricity by friction generated by raindrops falling and running off the surface of the solar panel.
A transparent layer containing the friction-electric nanogenerator is placed over a conventional solar panel. This nanogenerator converts friction — in this case caused by raindrops into electric energy.
The best thing is that these friction-powered solar panels can produce electricity at night if it rains.
Do Solar Panels Work On Cloudy Days?
Yes, solar panels work on cloudy days, too, but with a reduced output. Bifacial solar panels, for example, can use both direct and indirect sunlight. However, they are still the most productive when soaking up direct sunlight at midday.
On average, solar panels generate 10 to 25% of their normal power output on heavy overcast days.
However, if it starts to rain, you may be surprised to find that the output of your solar panels has increased.
The rain actually helps solar panels work more efficiently by washing away dust and debris from your solar panels so they can absorb sunlight more efficiently.
There are a few ways you can make solar panels still “work for you” on cloudy days.
You can add a solar battery to your home solar panels. The battery stores the surplus energy that your panels generate during the day so you can use it in less than ideal conditions, for example, on cloudy days and at night.
Another option is to use a net metering program. This program allows you to distribute excess power that your solar system generates into your municipal grid in exchange for credits from your utility company.
You can then cash in those credits to offset electricity costs on overcast days or at night and get more ROI out of your solar system.
Conclusion
Solar panels work by absorbing sunlight and converting it into electrical current. Each solar panel consists of multiple solar cells that, in turn, consist of thin layers of semiconductor material.
When sunlight particles strike the solar panel surface, they energize free electrons in solar cells. As each cell has a positive and negative charge, it creates an electric field that moves those electrons in one direction, effectively generating direct current.
This direct current then passes through the inverter, where it’s transformed into an alternating current that is suitable for home use.


