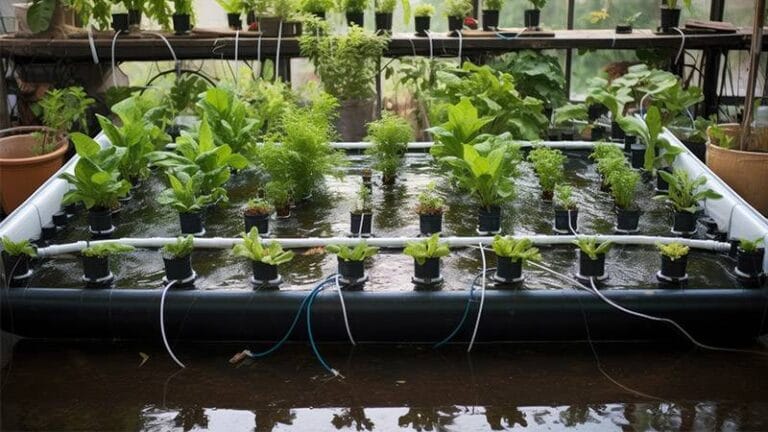
Imagine harvesting fresh vegetables and fish from your backyard, all year round.
Sounds like a dream, right? That’s the magic of an aquaponics greenhouse! By combining aquaculture and hydroponics, you create a symbiotic environment where fish and plants thrive together.
I stumbled upon this innovative method while searching for sustainable farming options.
Initially, it seemed complex, but once I got the hang of it, I was hooked. The process is fascinating and, believe it or not, quite simple once you understand the basics.
In this guide, I’ll walk you through the essentials of setting up your own aquaponics greenhouse. Whether you’re a gardening newbie or have a green thumb, there’s something here for everyone.
Let’s transform your home into a mini-ecosystem!
What Is Aquaponics?
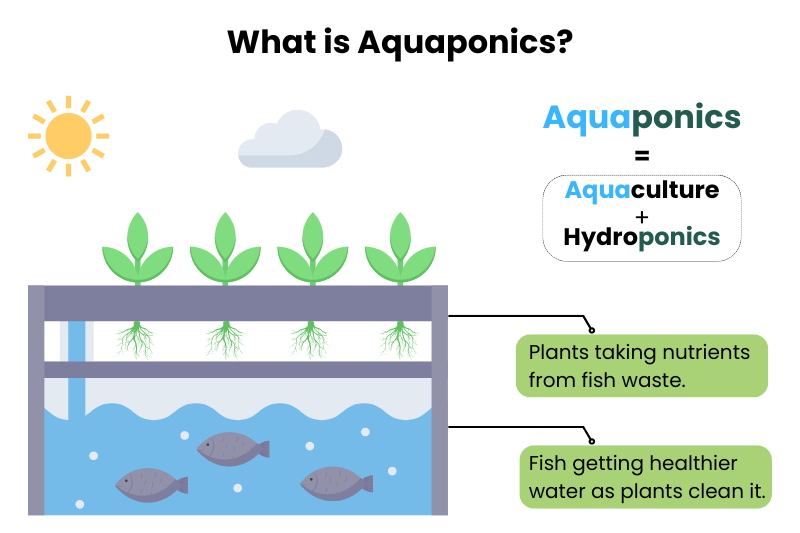
Aquaponics is an integrated farming method that combines aquaculture (raising fish) with hydroponics (growing plants without soil). Imagine a harmonious ecosystem where fish and plants help each other thrive.
A controlled greenhouse environment in an aquaponics greenhouse minimizes the invasion of pests, provides consistent temperatures for fish, and allows for more precise water circulation management, leading to healthier plants and fish.
When I first heard about aquaponics, it sounded like science fiction.
Fish waste provides nutrients for plants, and plants purify the water for the fish. This sustainable farming method creates a perfect balance.
The concept isn’t new, though. Ancient civilizations like the Aztecs used similar techniques called “Chinamaps.” With that method, they cultivated plants on floating rafts in shallow lakes. Today, aquaponics is making a comeback as a solution for eco-friendly farming.
Setting up an aquaponics system might seem daunting, but it’s simpler than you think. It’s a fantastic way to grow fresh produce and fish right in your backyard.
Still, for the complete newbies, I would suggest to start a hydroponics indoor garden first. It would be much easier to start with hydroponics before you move onto the world of aquaponics.
Basic Components of an Aquaponics System

Setting up an aquaponics system might seem like a big project. But breaking it down into its basic components, including water and air pumps for efficient water circulation, makes it easier.
Fish Tank
This is where your fish live and thrive. Common choices include tilapia and goldfish. My first tank housed some hardy goldfish, perfect for beginners.
Grow Bed
Here’s where the magic happens for plants. They absorb the nutrient-rich water provided by fish waste. Leafy greens and herbs are popular choices, but you can experiment with various plants.
Water Circulation System
You’ll need a pepper circulation system consisting of water and air pumps. Think of this as the heart of your system.
It pumps nutrient-laden water from the fish tank to the grow beds. After the plants absorb the nutrients, the now-clean water returns to the fish tank. I was amazed at how efficient this cycle is.
Bacteria
Beneficial bacteria are the unsung heroes, converting ammonia from fish waste into nitrates. These nitrates are a key nutrient source for plants. Without these bacteria, the system wouldn’t function properly.
In essence, fish feed the plants, and plants clean the water for the fish. This balanced cycle mimics nature, making aquaponics a fascinating and sustainable farming method.
Can You Do Aquaponics in a Greenhouse?

Absolutely! Combining aquaponics with a greenhouse is a fantastic idea. The greenhouse environment helps in keeping external pathogens at bay and reduces the chances of soil-borne diseases in aquaponics. It not only works but also enhances both systems’ efficiency.
You could check Pond Haven to get the necessary equipment to get started. Pond Haven partners with the top manufacturers to ensure the highest quality materials and equipment for your pond and aquaculture needs.
One major perk of a greenhouse is temperature control. Natural sunlight is crucial for plant growth in an aquaponics greenhouse. Fish like tilapia or koi prefer consistent temperatures, and a greenhouse provides just that.
I’ve seen how this stable environment keeps my fish happy and healthy, which means nutrient-rich water for the plants.
Another bonus is protection. A greenhouse shields your system from pests and diseases, reducing the need for chemicals. This aligns perfectly with organic farming principles.
I remember my first season – hardly any pests!
Greenhouses also allow precise water circulation management. Efficient water flow ensures plants get their nutrients while keeping the fish tank clean. It’s like having a mini-ecosystem in your backyard.
Combining aquaponics with a greenhouse boosts the benefits of both methods. You get healthier plants, happier fish, and increased yields. Plus, it’s a sustainable way to farm year-round, regardless of the weather outside.
If you’re into eco-friendly practices, this setup is a game-changer.
Pros and Cons of an Aquaponic Greenhouse
Combining aquaponics with a greenhouse offers numerous advantages, but it also has some drawbacks.
Let’s dive into the pros and cons of this innovative farming method.
Advantages of an Aquaponics Greenhouse

Year-Round Production
One of the biggest benefits is the ability to grow fresh produce and fish all year round. No more waiting for the right season. I remember harvesting fresh lettuce in the middle of winter – a delightful surprise!
Temperature Control
Greenhouses maintain consistent temperatures, which is crucial for fish like tilapia. They thrive in stable environments, leading to healthier fish and more nutrient-rich water for plants.
Pest and Disease Protection
Greenhouses provide a barrier against pests and diseases, reducing the need for chemical interventions. This aligns perfectly with organic farming practices. My plants have never looked healthier since moving to a greenhouse setup.
Efficient Water Use
Aquaponics systems use about 90% less water than traditional farming. The water is continuously recycled between the fish tank and grow beds, making it a very efficient method.
High Yields
One of the main benefits of combining aquaponics with a greenhouse is the potential for high yields. The controlled environment allows for year-round production, and the symbiotic relationship between fish and plants can lead to faster growth rates.
Additionally, utilizing vertical space for growing climbing plants can significantly increase production levels.
Energy Use
While greenhouses can help regulate temperature and extend growing seasons, they can also be energy-intensive.
Managing the energy use efficiently is crucial to keep operational costs down. Another challenge is dealing with too much direct light, which can lead to excessive algae growth and negatively impact fish and plant health.
Proper insulation and a well-designed greenhouse are essential to protect the system from extreme temperatures and light exposure.
Educational Opportunities
Setting up and maintaining an aquaponics greenhouse is a great educational experience. It’s fascinating to learn about the symbiotic relationships between fish and plants.
My kids love helping out and learning about sustainable farming.
Disadvantages of an Aquaponics Greenhouse
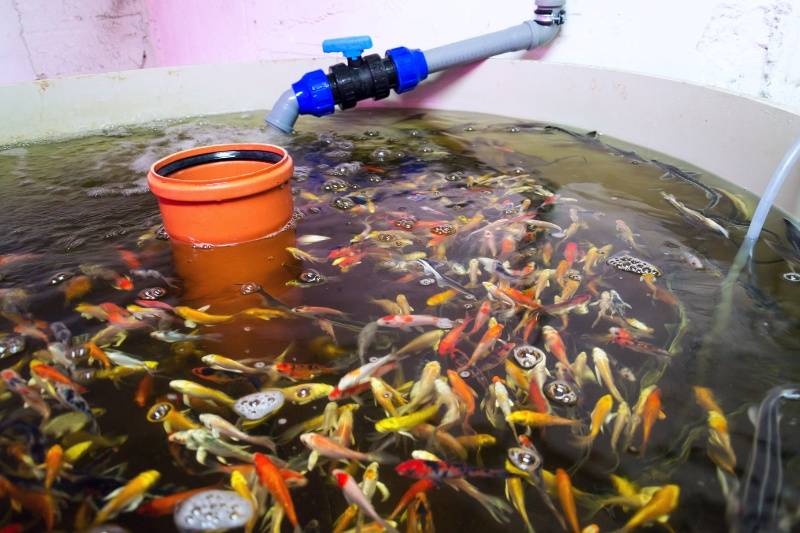

Initial Setup Cost
Setting up an aquaponics greenhouse can be expensive. The cost of the greenhouse, tanks, pumps, and other equipment can add up. However, it’s an investment that pays off over time.
Maintenance
While aquaponics systems are efficient, they require regular maintenance. You need to monitor water quality, feed the fish, and ensure everything is running smoothly. It’s not a set-it-and-forget-it system.
Energy Use
Greenhouses can require significant energy, especially in colder climates where heating is necessary. This can increase your overall costs and carbon footprint.
Complexity
Aquaponics systems can be complex to set up and manage, especially for beginners. There’s a learning curve involved. I remember feeling overwhelmed at first, but with patience and research, I got the hang of it.
Fish Care
Caring for fish adds another layer of responsibility. You need to ensure they are healthy and well-fed. If the fish are stressed or sick, it can affect the entire system.
Space Requirement
Aquaponics greenhouses require a decent amount of space. If you have a small backyard, fitting everything in can be a challenge.
Risk of System Failure
If one component of the system fails, it can affect the entire setup. For example, if the pump stops working, it can disrupt the water flow, harming both the fish and plants.
Considerations for Aquaponics Greenhouses

Starting an aquaponics greenhouse is an exciting venture, but proper planning is crucial. Here’s a checklist to help you cover all bases.
Location
Choose a sunny spot for your greenhouse. Plants need ample sunlight to grow well. Make sure it’s easily accessible for regular maintenance and shielded from strong winds and flooding. I found a spot in my backyard that met these criteria perfectly.
Water Source
Water quality is vital. Avoid chlorinated water directly; it can harm fish. Ensure a consistent and clean water source. I use rainwater collected in barrels, which works great.
Fish Selection
Pick fish that thrive in your climate. Tilapia is a popular choice due to its hardiness and fast growth. Research their needs thoroughly. I started with goldfish, which are easy to care for.
Plant Selection
Choosing the right plants for your aquaponics system is essential. Consider plants that thrive in a water-based environment and are compatible with your fish species.
Opt for plants suitable for aquaponics like leafy greens and herbs. Avoid root vegetables, as they can be tricky.
If you’re planning to sell produce, consider what’s in demand locally. My lettuce and basil have been a hit at the local farmers’ market.
System Design
Designing your aquaponics system involves selecting the right type of greenhouse. Different greenhouse designs have their own advantages and limitations in relation to aquaponics setups. For instance, some designs offer better space utilization and protection against weather conditions.
Whether for personal use or commercial purposes, make sure it’s adaptable for future expansions. My initial setup was small, but I’ve added more grow beds over time.
Budget
Factor in all costs: greenhouse setup, equipment, fish, and plants. Don’t forget ongoing expenses like electricity and fish feed. My initial investment was substantial, but the returns have been worth it.
Training and Knowledge
Invest time in learning about aquaponics and greenhouse management. Attend workshops or courses if possible. Good reference materials are invaluable. I’ve found online forums and local clubs to be great resources.
Backup Systems
Have a backup power solution to prevent system failures during outages. Establish procedures for potential issues like disease outbreaks or equipment malfunctions. I keep a generator handy and have a plan for emergencies.
What Type of Greenhouse is Ideal for an Aquaponics System?
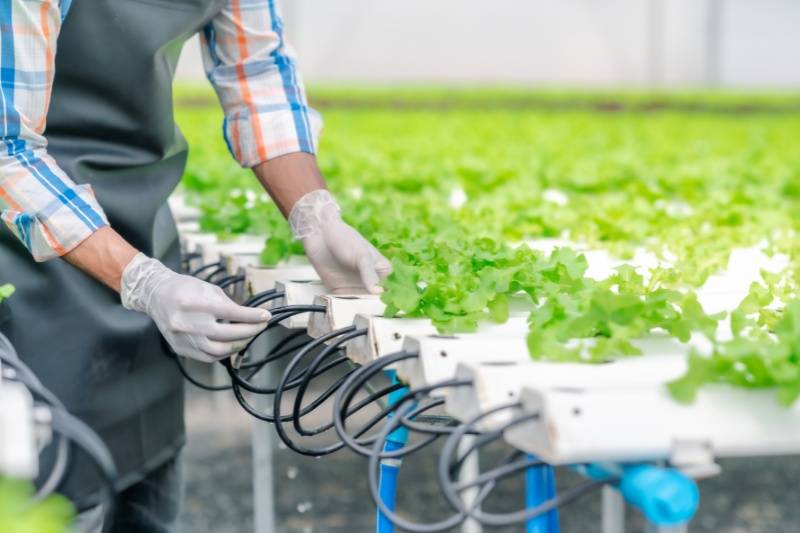

The success of your first aquaponics system depends largely on the greenhouse you choose. Aquaponic systems create a controlled environment for reducing the need for chemical pesticides and providing an ideal habitat for fish tanks within greenhouses. A passive solar greenhouse is often ideal.
These greenhouses have an insulated north wall and glazing facing the south, maximizing sunlight exposure.
I opted for this type of greenhouse, and it has made a significant difference. The south-facing glazing ensures my plants get plenty of light, especially in winter. This design keeps the temperature stable, which is perfect for my tilapia.
Another benefit is the insulated north wall. It helps maintain a warm environment year-round, reducing the need for additional heating. This was a game-changer during the colder months.
Consider the greenhouse size as well. Ensure it’s spacious enough to accommodate your fish tanks and grow beds comfortably. My initial setup was a bit cramped, but expanding the greenhouse solved that issue.
Ventilation is another critical factor. Proper airflow prevents humidity buildup and keeps plants and fish healthy. I installed vents and fans, which made a noticeable difference in maintaining the right environment.
Considering all the facts, a passive solar greenhouse with good insulation, adequate size, and proper ventilation is ideal for an aquaponics system. It ensures optimal growing conditions and stable temperatures, benefiting both plants and fish.
Tips for Designing an Aquaponics Greenhouse
Designing an aquaponics greenhouse requires a blend of creativity and practicality. It’s not just about housing plants and fish; it’s about creating a harmonious environment where both can thrive. Here are some essential tips to consider when designing your aquaponics greenhouse:
Optimize Space
Make the most of the available area by considering vertical farming techniques. This allows for the cultivation of more plants without compromising on the space needed for fish tanks. Remember, a well-planned layout can significantly boost your yield.
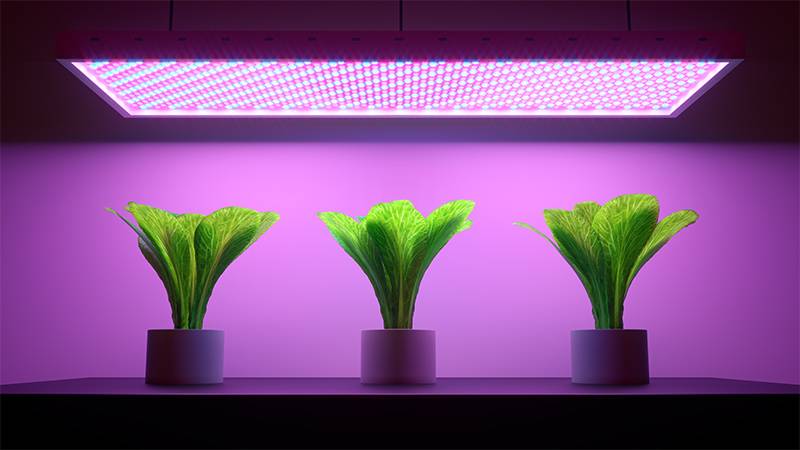
Ensure Proper Lighting
While natural sunlight is the best source of light for plants, sometimes it might not be enough, especially during shorter winter days. Consider supplemental lighting options, such as LED grow lights, to ensure your plants receive the necessary light for photosynthesis.

Maintain Temperature
Fish and plants have specific temperature needs. Invest in a good quality heating or cooling system to regulate the greenhouse’s temperature. Automated systems can monitor and adjust the temperature, ensuring it remains within the desired range.

Incorporate Efficient Water Circulation
An efficient water circulation system is the heart of an aquaponics setup. Ensure that the water, filled with nutrients from fish waste, is continuously pumped from the fish tank to the grow beds and back.
Plan for Ventilation
Proper ventilation is crucial to prevent overheating and ensure a continuous supply of fresh air. Consider installing roof vents or automated exhaust fans to maintain optimal air circulation.

Choose Suitable Flooring
While gravel or porous concrete can be ideal for drainage, consider the ease of cleaning and maintenance. A clean floor reduces the risk of pests and diseases.
Accessibility
Design your greenhouse in a way that all areas are easily accessible. This will make tasks like feeding fish, harvesting plants, or performing maintenance checks much more manageable.
Safety First
Ensure all electrical installations, like pumps or lights, are safely installed. Waterproofing and using ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) can prevent potential electrical hazards.
How to Build Your Own Aquaponics Greenhouse
Building your own aquaponics greenhouse is a rewarding project, allowing you to grow fresh produce and fish sustainably.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to set up your aquaponics haven.
1. Select the Right Location
Start by picking a spot with ample sunlight, ideally 6-8 hours a day. Ensure it’s shielded from strong winds and potential flooding. Accessibility for regular maintenance is key. I chose a sunny corner of my backyard that’s easy to reach.
2. Choose the Greenhouse Structure
Decide on the type of greenhouse based on your budget, space, and climate. Options include Hoop Houses, A-Frames, or Geodesic Domes. I went with an A-Frame due to its simplicity and strength.
3. Lay the Foundation
Prepare the ground by removing debris and leveling it. Consider laying gravel or porous concrete for good drainage. A sturdy foundation is crucial to support the fish tanks and grow beds. I found this step essential for stability.
4. Construct the Greenhouse
Follow the instructions for your chosen greenhouse type. Ensure the structure is stable and all joints are sealed to maintain temperature and humidity. Use PVC pipe for the framework if you’re building a Hoop House.
My first greenhouse build was a learning experience, but sealing the joints made a big difference.
5. Set Up the Aquaponics System
- Fish Tank: Place the fish tank where it's easily accessible. Ensure it's level and stable. Mine sits snugly against the north wall for added insulation.
- Grow Beds: Position the grow beds above or next to the fish tank, depending on your design. Use a medium like expanded clay pellets or gravel. My grow beds are right above the tank, making water circulation easier.
- Water Circulation: Install a pump to move water from the fish tank to the grow beds. Ensure there’s a return system to channel water back to the fish tank. I used gravity for the return, which saved on pump costs.
6. Introduce Beneficial Bacteria
Before adding fish and plants, establish beneficial bacteria. These convert ammonia from fish waste into nitrates for plants. Kickstart this by adding a bacteria starter or a few fish, gradually increasing the number. This step ensures a healthy system from the start.
7. Plant and Fish Selection
Choose plants and fish suitable for your climate. Leafy greens, herbs, and certain fruits are great for beginners. Tilapia, Koi, goldfish, or catfish are popular fish choices. I started with tilapia and lettuce, both hardy and forgiving.
8. Monitor and Adjust
Regularly check water pH levels, aiming for 6.8 to 7.2. Monitor fish and plant health, adjusting feeding rates and checking for pests or diseases. Keeping a log helped me track and troubleshoot any issues.
9. Install Supplemental Systems
Consider heating, lighting, or ventilation systems depending on your region. These optimize growth conditions. I added supplemental lighting for winter months, which kept my plants thriving.
10. Regular Maintenance
Clean the fish tank, check the water circulation system, and prune plants as needed. Regular maintenance ensures longevity and efficiency. Setting a weekly routine made this manageable for me.
11. Harvest and Enjoy
Once plants mature, harvest them and enjoy fresh, organic produce. If you have edible fish, they can be harvested when they reach the desired size. There’s nothing like eating a meal you’ve grown yourself!
Best of Luck with Your Aquaponics Greenhouse!
Starting an aquaponics greenhouse is a fantastic way to grow your own food sustainably.
By combining the principles of aquaculture and hydroponics, you create a self-sustaining ecosystem that produces fresh fish and vegetables year-round. With careful planning, regular maintenance, and a bit of patience, you can enjoy the rewards of this innovative farming method.
So, gather your materials, choose the perfect spot, and start building your aquaponics greenhouse today. Embrace this journey towards a greener, more self-sufficient lifestyle.
Your homegrown produce and fish await!

